Understanding Inflammation and How it happens: Can Liquid Turmeric Help?
Inflammation is a natural process in our body that helps to protect and heal us from injuries and infections. However, when inflammation becomes chronic, it can lead to a host of health problems, from heart disease to arthritis. In this guide, we will explore what inflammation is, why it happens, and how you can take steps to reduce chronic inflammation in your body.
What is Inflammation?
Inflammation is a natural response of the body to injury or infection. When we get a cut, for example, our immune system sends specialized cells to the site of the injury to repair the damage and fight off any potential infections. This is known as acute inflammation, and it usually goes away on its own once the injury or infection has been resolved.
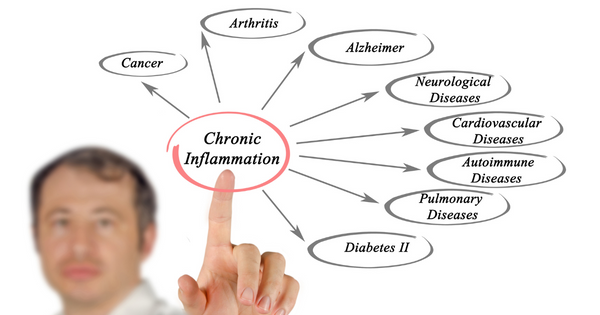
However, when inflammation persists, it can lead to chronic inflammation, which can damage tissues and organs in the body. Chronic inflammation has been linked to a wide range of health problems, including heart disease, stroke, cancer, diabetes, and Alzheimer's disease.
One interesting fact is that chronic inflammation has been shown to accelerate the aging process. This is because chronic inflammation can damage DNA and cause cellular dysfunction, leading to premature aging and a higher risk of age-related diseases.
Why Does Inflammation Happen?
Inflammation is a complex process that involves many different cells, molecules, and signaling pathways in the body. It is triggered by a wide range of stimuli, including infections, injuries, and exposure to environmental toxins.
As we age, our immune system may become less effective at controlling inflammation, leading to chronic inflammation. Poor diet, lack of exercise, chronic stress, and exposure to environmental toxins can also contribute to chronic inflammation.
Inflammation happens as a natural response of the body to injury or infection. When there is an injury or infection, the body's immune system triggers a cascade of events that lead to inflammation. This is the body's way of defending itself and initiating the healing process.
When the immune system detects an injury or infection, it releases a variety of chemicals, including histamine, bradykinin, and prostaglandins. These chemicals cause the blood vessels to dilate, increasing blood flow to the affected area. This increased blood flow can cause redness, warmth, and swelling, as well as pain and discomfort.
Chronic inflammation has been linked to a wide range of health problems, including heart disease, diabetes, cancer, and autoimmune disorders. In fact, inflammation is now considered to be a root cause of many of these diseases.
What is the difference between acute inflammation and chronic inflammation and why does it matter?
Acute inflammation:
Acute inflammation is a normal and healthy response of the body to injury or infection. It helps to protect the body from further harm and initiate the healing process. Acute inflammation is usually a short-term response that resolves once the injury or infection is healed.

Chronic inflammation:
On the other hand, chronic inflammation is a prolonged and persistent inflammatory response that lasts for weeks, months, or even years.
Chronic inflammation can damage tissues and organs in the body, leading to a range of health problems, including heart disease, stroke, cancer, diabetes, and Alzheimer's disease.
But it's not all doom and gloom! By understanding inflammation and what triggers it, we can take steps to reduce our risk of chronic inflammation and the associated health problems.
One of the biggest factors contributing to chronic inflammation is diet. The Western diet, which is high in refined carbohydrates, processed foods, and unhealthy fats, has been shown to promote inflammation in the body. On the other hand, a diet that is rich in whole, plant-based foods, healthy fats, and lean protein can help reduce inflammation.
Exercise is another important factor in reducing inflammation. Regular physical activity has been shown to reduce levels of inflammatory markers in the body and improve overall health. In fact, exercise is so effective at reducing inflammation that it has been called a "natural anti-inflammatory."
Chronic stress can also contribute to inflammation in the body. When we are under stress, our bodies release stress hormones that can trigger inflammation. Finding ways to manage stress, such as through mindfulness practices, yoga, or meditation, can help reduce inflammation and improve overall health.
Finally, exposure to environmental toxins, such as air pollution and chemicals in household products, can also contribute to chronic inflammation. Reducing exposure to these toxins and choosing natural, non-toxic products can help reduce inflammation and improve overall health.
By understanding inflammation and taking steps to reduce our risk of chronic inflammation, we can improve our overall health and reduce our risk of chronic diseases. So, let's make healthy choices in our diet, exercise regularly, manage our stress, and choose non-toxic products to reduce our exposure to environmental toxins. Small changes can make a big difference in our health!

What are the Symptoms of inflammation?
The symptoms of inflammation can vary depending on the location and severity of the inflammation. Common symptoms of inflammation include redness, swelling, pain, heat, and loss of function. For example, if inflammation occurs in the joints, it can cause stiffness, pain, and difficulty moving. Inflammation in the digestive system can cause bloating, diarrhea, and abdominal pain. Chronic inflammation can also lead to fatigue, fever, and weight loss.
Inflammation can manifest in a variety of ways, depending on the location and severity of the inflammation. Some common symptoms of inflammation include:
- Redness: Inflammation can cause affected areas to become red or discolored due to increased blood flow.
- Swelling: Swelling is a common sign of inflammation, as it results from increased fluid accumulation in the affected area.
- Pain: Inflammation can cause pain or tenderness in the affected area, which can range from mild to severe.
- Heat: Inflammation can cause the affected area to feel warm or even hot to the touch.
- Loss of function: Inflammation can also cause a loss of function in the affected area, such as difficulty moving a joint or impaired breathing.
It's important to note that inflammation can also occur internally, without any visible external symptoms. This is why it's important to be aware of other symptoms of chronic inflammation, such as fatigue, fever, and weight loss.

Why Take Liquid Turmeric For Inflammation?
Liquid turmeric has been shown to have anti-inflammatory properties that can help reduce inflammation in the body. Turmeric contains a compound called curcumin, which has been found to inhibit the production of inflammatory molecules in the body. In addition, curcumin has been shown to have antioxidant properties, which can help protect the body against oxidative stress and damage caused by free radicals.
Curcumin, the active compound in turmeric, has been studied for its anti-inflammatory effects on the body. It works by blocking the activity of inflammatory enzymes in the body, thereby reducing inflammation. Several studies have shown that curcumin can be as effective as some anti-inflammatory drugs in treating acute inflammation, such as in cases of post-surgical inflammation or inflammation caused by rheumatoid arthritis.
In addition to its anti-inflammatory properties, curcumin has been shown to have antioxidant properties that can help reduce oxidative stress and damage caused by free radicals. Oxidative stress is a process in which the body's cells are damaged by harmful molecules called free radicals, which can contribute to the development of chronic diseases such as cancer, heart disease, and Alzheimer's disease.
One of the advantages of taking liquid turmeric over other forms of turmeric supplements is that it is more easily absorbed by the body. Liquid turmeric can bypass the digestive system and be absorbed directly into the bloodstream, allowing for faster and more efficient absorption of the curcumin.



























